4. Modules overview
The named modules below extend the core functionality of AGX Dynamics to cover a wide range of simulation needs.
4.1. AGX Cable
License |
AgX-Cable |
|---|---|
Library |
agxCable.lib |
Namespace |
agxCable |
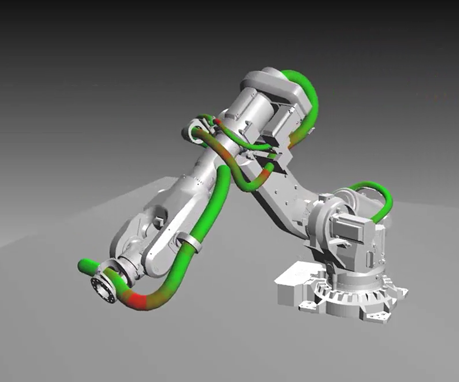
The AGX Cable module can be used to simulate hoses, ropes, dress packs, and of course, cables. These are long structures with a circular cross section that can be bent, stretched and twisted. Modeled with discrete elements that can be subjected to large displacement. AGX Cables can interact with all other AGX geometry shapes, including itself and other cables. Robot dress packs analysis is a particularly relevant application.
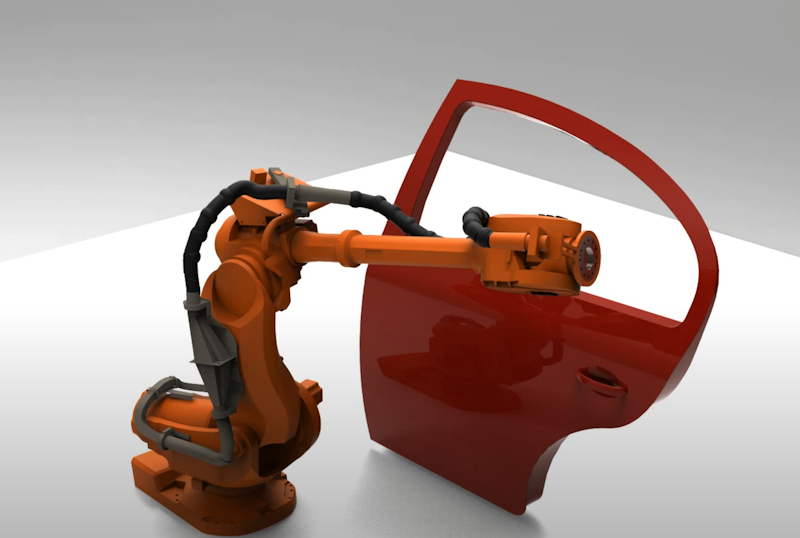

Features:
High-fidelity self interaction
Arbitrary stiffness and damping for torsion, bend, and stretch
Support for plastic deformation
Internal force reporting
Fully integrated with other modules including hydrodynamics
Easy routing along list of points in space
Initial state can be configured with any shape
4.2. AGX Cable Damage
License |
AgX-CableDamage |
|---|---|
Library |
agxCable.lib |
Namespace |
agxCable |
Building upon AGX Cable, the AGX Cable Damage module provides computations to estimate wear and damage caused on a cable during the simulation and provide an aggregate report. All types of deformations are considered such as stretch, bend, and twist, along with deformation rates and what forces caused them. These are aggregated according to a configurable set of weights. This greatly assists the optimization of controllers and dresspack routing during development, or analyze problems and identify their causes after deployment.
Features:
Helps tune controllers to minimize damage
Accounts for stretch, bend, twist, and their rates
Accounts for internal and external forces
Accounts for contacts and friction
Configurable damage metric
Live and postmortem analysis
Perfect for robot programming and design
4.3. AGX Control
License |
AgX-Control |
|---|---|
Library |
agxModel.lib |
Namespace |
agxControl, agxModel |
The AGX Control module provides functionality related to controlling mechanical systems such as vehicles and machines. Specifically, it contains forward kinematics, inverse kinematics and inverse dynamics. In addition it also contains functionality for Pure Pursuit path tracking for vehicles.
Related to this is also the library for PID controllers.
agxModel::ReconfigureRequest is another related functionality that allows for reconfiguring a complex mechanical system via a dynamic simulation. A wheel loader for example, you might want to transform the bucket to a specific transform, the rest of the machine should then adopt to this new configuration in a physically correct way, including ranges etc.
Features:
Inverse kinematics for robotic systems
Inverse dynamics for robotic systems
PID Controllers
Pure Pursuit path tracking for vehicles
Dynamic reconfiguration of mechanical systems
4.4. AGX ROS2
License |
None |
|---|---|
Library |
agxROS2.lib |
Namespace |
agxROS2 |
The ROS2 module for AGX Dynamics provides seamless integration between AGX Dynamics simulations and the Robot Operating System 2 (ROS2) framework. This module enables users to leverage ROS2’s powerful communication and middleware capabilities to control and monitor AGX Dynamics simulations in real-time.
Subscribers and Publishers for standard messages.
Support for Sensor (Lidar) data publishing.
Self contained: Does not depend on any ROS2 installation.
4.5. AGX DriveTrain
License |
AgX-DriveTrain |
|---|---|
Library |
agxModel.lib |
Namespace |
agxDriveTrain, agxPowerLine |
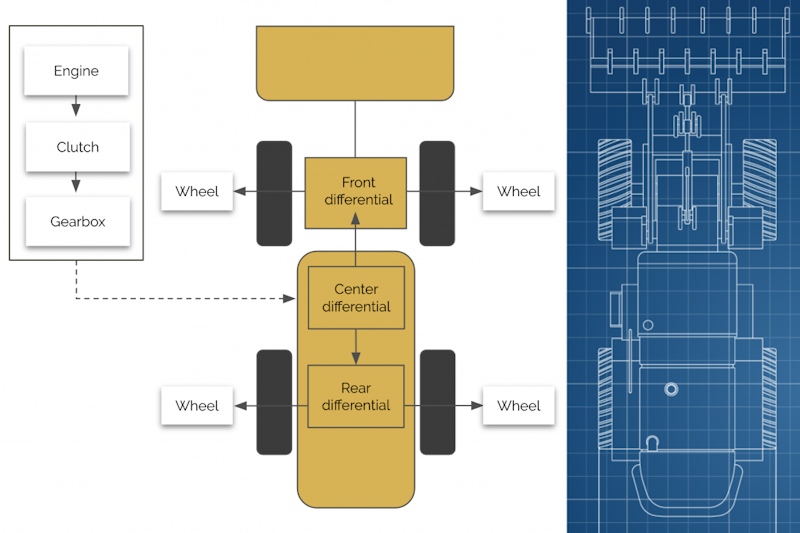
The AGX DriveTrain module simulates the 1D dynamics of mechanical components such as shafts, gears, differentials, and clutches in tight coupling with full 3D multi-body dynamics. AGX DriveTrain offers engine models via torque versus RPM lookup table or with a more accurate, first-principle diesel engine model. The module can be used with any AGX Dynamics model and in conjunction with any other modules to power excavators, trucks, winches, and robots, even to power a hydraulic pump.
Features:
Components for building a complete drivetrain: shaft, clutch, gear box, brake, differential and more
Combustion engine model
Torque/RPM engine model
DC electric motor
Deep integration with multi-body dynamics: Connect drivetrain directly to rotational or linear constraints
Wire winch support
Integrated with AGX Hydraulics
4.6. AGX Hydraulics
License |
AgX-Hydraulics |
|---|---|
Library |
agxModel.lib |
Namespace |
agxHydraulics |
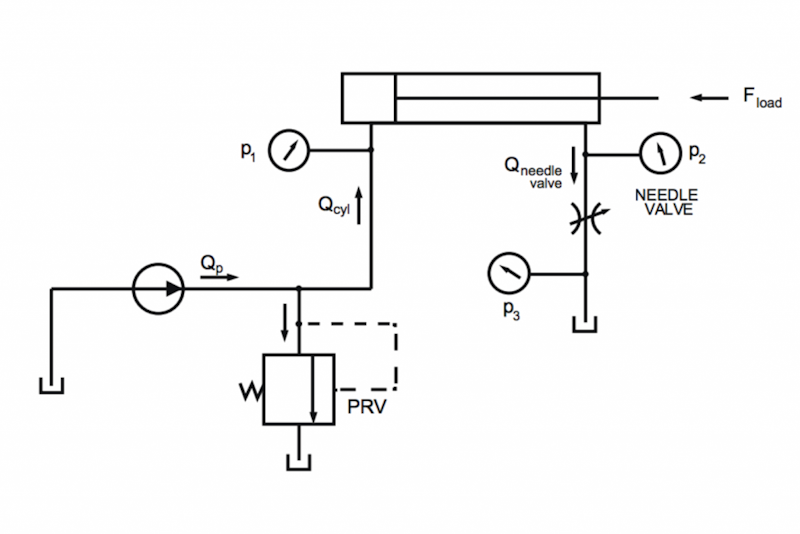
AGX Hydraulics is a 1D simulation of hydraulic systems tightly coupled to the multi-body simulation in 3D. Components for building hydraulic systems integrated with mechanics include: accumulator, binary valves, check valves, motors, pumps (both fixed and variable displacement), stop valves, needle valve, and relief valve. It integrates with the AGX Drivetrain module, allowing for modeling of mixed mechanical and hydraulic systems. Coupling to mechanical simulation is done through linear and rotational actuators, enabling simulation of complete hydraulic-powered systems such as hydraulic winches, excavators, cranes, and wheel loaders.
Features:
Integrated simulation/coupling of 1D hydraulics and 3D multi-body dynamics using the same solver: allows for large time steps and robust simulation
Handles stiff interaction between hydraulics and mechanical simulation
Fast and efficient
Library of basic hydraulic components: pump, motor, valves, accumulator, actuator
4.7. AGX Granular
License |
AgX-Particles |
|---|---|
Library |
agxPhysics.lib |
Namespace |
agx, agx::Physics |
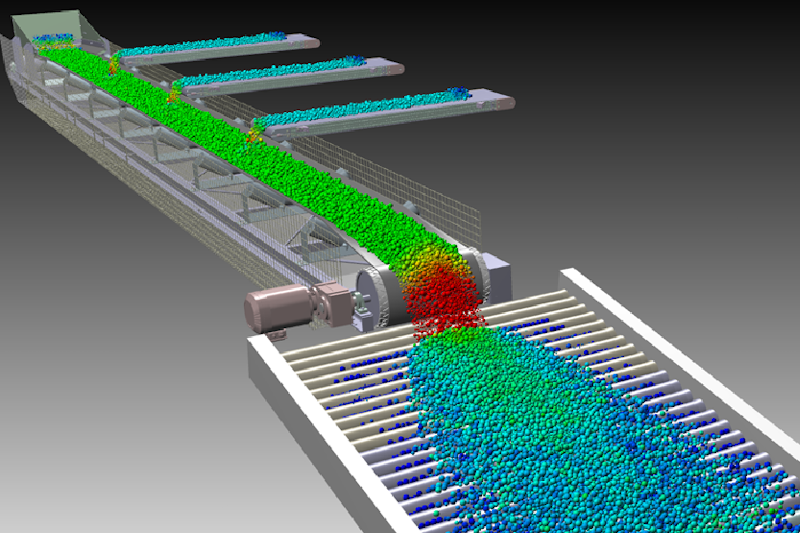
With the AGX Granular module, you can study and optimize the design and control of systems that transport and process granules in bulk—rocks, pellets, pills, or grains. Material flow speed and evenness are fundamental to efficiency, leading to significant savings in time, energy, and improved quality. AGX Granular uses the Non-smooth Discrete Element Method (NDEM) instead of conventional Discrete Element Method (DEM), meaning it is deeply integrated with core models and numerical methods at the heart of AGX Dynamics. The core multi-body and specialized granular solvers are strongly coupled, leading to accurate coupling forces between granules and mechanical systems and very stable simulations. Simulating a pelleting drum with hundreds of thousands of pellets or a fully loaded dumper truck can be done at large time steps with full confidence.
The AGX Granular module is also available in a separate product in a full CAD environment. For more information see Algoryx Momentum.
Features:
Large time-step integration
Stable, accurate integration with multibody dynamics
High-performance parallel solver
Linear and Hertzian contact models
Rolling resistance for stable piles
Statistics output and sensors
Support for recording and playback of simulations (Journal files).
Journal Viewer with UI for analysis of recorded simulations
Force visualization
Python scripts for analysis and data export
4.8. AGX Hydrodynamics & Aerodynamics
License |
AgX-Hydrodynamics |
|---|---|
Library |
agxModel.lib |
Namespace |
agxModel |
The AGX Hydrodynamics module computes drag and lift forces on any geometry due to water or air directly from the 3D tessellation and accounting for water level. As every triangle is accounted for, the forces are as accurate as the geometric representation. This is essential for simulating ROVs, submarines, anchors and oil rigs, as well as cranes in heavy wind conditions and wind turbines. It is fully integrated with AGX Wire and AGX Cable modules.
Features:
Computes lift, drag, and buoyancy forces
Includes hydrodynamic added mass
Works directly on the geometry
Accounts for dynamic waterline at each simulation step
User-defined wind or water currents
4.9. AGX Sensor
License |
AgX-Sensor |
|---|---|
Library |
agxSensor.lib |
Namespace |
agxSensor |
AGX Sensor is a module of sensors and utilities for simulating physically accurate real-time sensor readings coupled to the multi-body simulation. It contains a set of convenient-to-use sensor types, which can easily be configured directly from real-world sensor data sheets. These sensors reside in a sensor environment that contains all objects detectable by the sensors and all environmental parameters, such as fog, rain, dust, surface materials, and magnetic fields, in a way that does not interfere with the main multi-body simulation. This module integrates with the AGX Terrain module, allowing sensors to detect terrain changes in real-time.
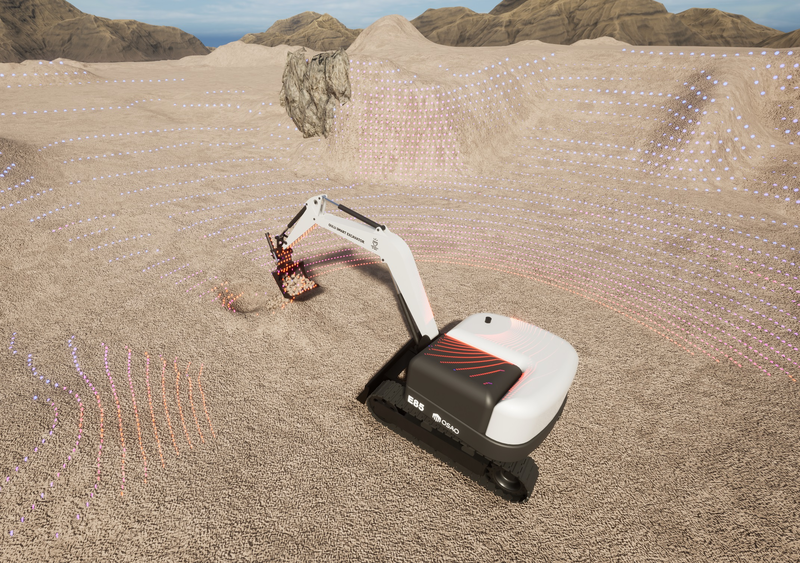

Sensor Types:
LiDAR
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
Accelerometer
Gyroscope
Magnetometer
4.10. AGX Terrain
License |
AgX-Terrain |
|---|---|
Library |
agxTerrain.lib |
Namespace |
agxTerrain |
The AGX Terrain module simulates soil deformation via interactions with wheels, tracks, blades, buckets, and shovels. Useful for bulldozers, excavators, wheel loaders, and track vehicles, it supports excavation, grading, and all forms of contacts, including all sides of any tool. It rigorously conserves mass and accounts for compaction and soil failure. It includes a calibrated, configurable library of soil models for gravel, sand, and dirt. Most importantly, this module computes accurate bi-directional forces between contacting bodies, tools, and terrain—crucially relevant for machine learning applications when developing autonomous machinery.
With Terrain Paging, only the proximity of the terrain near a vehicle is active at one time, allowing for unlimited working areas.
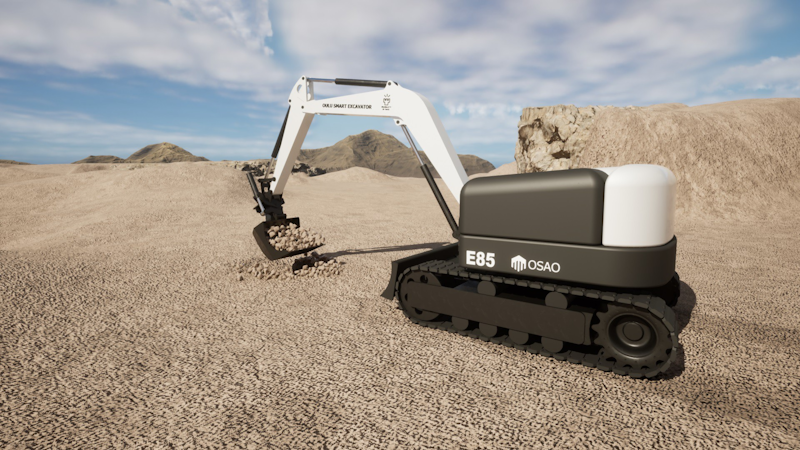

Features:
Real-time performance
Accurate soil mechanics with compaction
Accurate calculation of interaction forces
Strong coupling with all of AGX Dynamics
Support for dozer blades, buckets, shovels, tires, and tracks
Excavation, grading, and compaction capabilities
Extensible and configurable terrain material library
Supports terrain paging for unlimited terrain size
4.11. AGX Tire
License |
AgX-Tires |
|---|---|
Library |
agxModel.lib, agxVehicle.lib |
Namespace |
agxModel, agxVehicle |
The Two body Tire module adds flexibility to otherwise rigid wheels to represent tires. The model introduces elasticity, slip, and anisotropic friction in forward and transversal directions. AGX Tire works for on and off-road scenarios. Related to this is also the agxVehicle::WheelJoint and the various steering models that can be used to simulate realistic suspension and steering behavior.

Features:
Independent forward and sideways friction
Elasticity and damping in radial, torsional, and lateral directions
Fast and efficient
4.12. AGX Tracks
License |
AgX-Tracks |
|---|---|
Library |
agxVehicle.lib |
Namespace |
agxVehicle |
The AGX Tracks module allows for simulation of crawler/tracked vehicles or dynamic conveyor belts. The model contains a routing algorithm that automatically sets up the geometrical configuration of the tracks, including initial tension. An automatic model reduction system ensures performance is retained even for a large number of treads or shoes, and it allows for varying geometry setup over the length of the track. Suitable for bulldozers, wheel loaders, and any tracked vehicle.
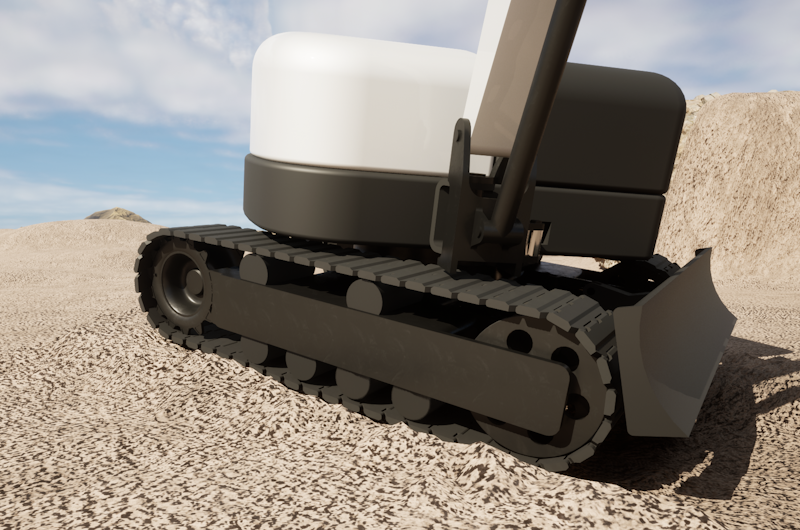

Features:
Automatic routing for easy setup
Works with AGX Terrain
Variable pad configuration
Two track models, one for slow moving vehicles with high fidelity and one for fast moving vehicles with high performance.
Can also be used to simulate conveyor belts
4.13. AGX Wire
License |
AgX-Wire |
|---|---|
Library |
agxPhysics.lib |
Namespace |
agxWire |
Like cables, wires have stretch and bend resistance but differ in having no resistance to torsion. They also have dynamic resolution, allowing them to be kilometers long and subjected to arbitrarily high tension. The resolution is adapted according to contact geometry so they can be wrapped around other objects, including other wires. They are used for cranes, anchor handling, winching, tethers, and umbilicals for ROVs and other sub-sea operations. Wires can be tuned to represent ropes, wires, and chains. AGX Wire has proven itself in mission-critical simulators around the globe for almost two decades.

Features:
Detailed material specifications
Capable of handling extreme mass ratios
Tension and bend force reporting
Responds to wind and hydrodynamics
Winches with speed and tension control
DriveTrain and Hydraulics can power winches
Wires make contact with all other objects
Dynamic configuration: cut, merge, split, and attach objects during runtime